- Feature
- Performance
- Curve Comparison Chart
- Advantage
- Applications
- Video
Feature
Feature Description
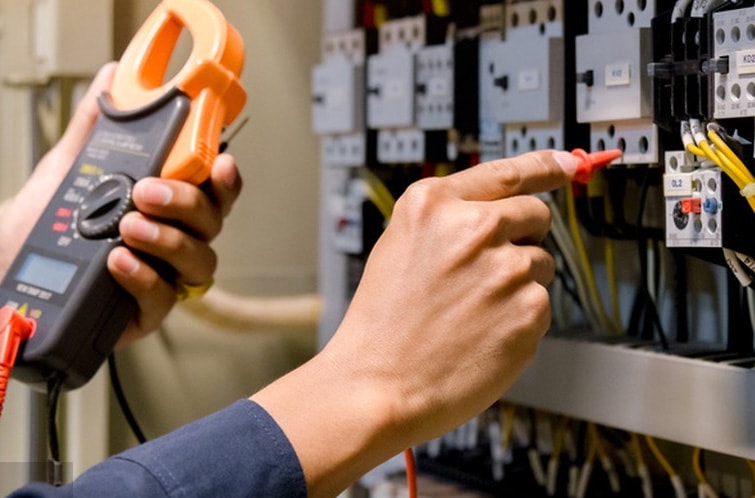
Material: Fe-based nanocrystalline;
Low magnetostriction coefficient - Compared to traditional magnetic materials, low noise;
Low cost - Compared to permalloy, it has high cost-effectiveness and can be replaced;
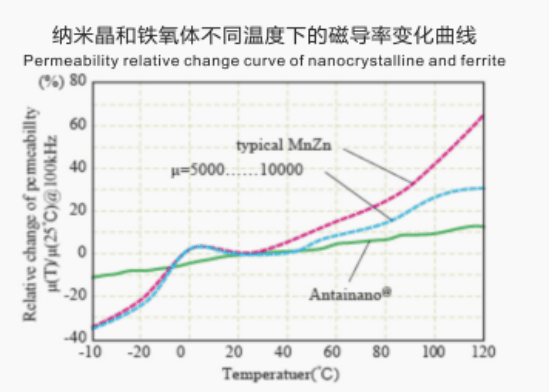
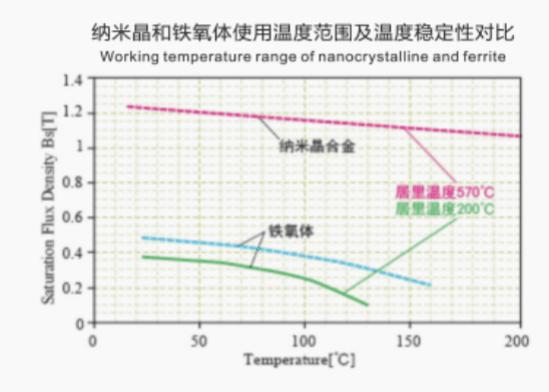
Excellent thermal stability - with small performance deviation in a wide temperature range of -20 ℃ to 120 ℃.

Performance

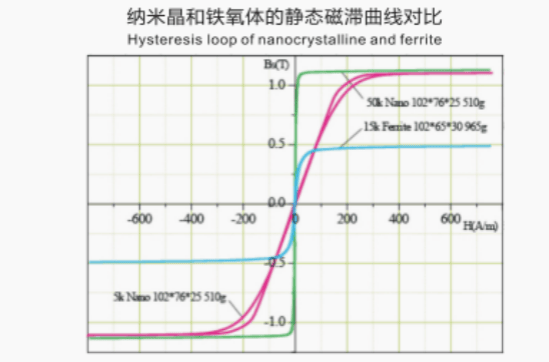
Low core losses
Nanocrystalline cores have low core losses, resulting in reduced energy dissipation during magnetic field variations. This characteristic allows for improved efficiency and performance, especially in high-frequency applications.
High saturation magnetic induction
Nanocrystalline cores offer high saturation magnetic induction, which means they can operate at higher magnetic field strengths without saturating. This allows for efficient handling of larger currents and higher power levels.
Wide frequency bandwidth
Nanocrystalline cores exhibit a wide frequency bandwidth, enabling them to operate effectively across a broad range of frequencies. This makes them suitable for applications in power electronics, telecommunications, and other fields where a wide frequency response is required.
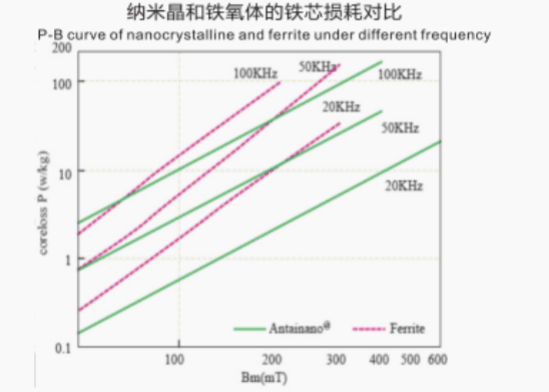
Excellent temperature stability
Nanocrystalline cores offer excellent temperature stability, maintaining their magnetic properties even at high temperatures. This feature makes them suitable for applications that involve high-temperature environments, such as power transformers and inverters.
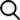
Curve Comparison Chart
Advantage
-
01
High magnetic permeability
Nanocrystalline cores exhibit extremely high magnetic permeability, which allows for efficient magnetic flux coupling and transfer. This high permeability enables the cores to store and transfer magnetic energy more effectively, resulting in improved performance and reduced losses in applications such as transformers and inductors.
-
02
Low core loss
Nanocrystalline cores have significantly lower core losses compared to other magnetic core materials. This is due to the unique structure of nanocrystalline alloys, which consist of tiny crystalline grains separated by grain boundaries. These grain boundaries impede the movement of magnetic domain walls, reducing eddy current and hysteresis losses. The low core losses result in higher energy efficiency and reduced heating in magnetic components.
-
03
Wide operating frequency range
Nanocrystalline cores exhibit excellent performance across a wide range of frequencies. They have a high permeability over a broad frequency spectrum, making them suitable for applications that require operation at high frequencies, such as power electronics, telecommunications, and high-frequency transformers.
-
04
Good temperature stability
Nanocrystalline magnetic cores have excellent temperature stability, maintaining their magnetic properties even at elevated operating temperatures. This stability makes them ideal for applications that involve high-temperature environments, as they can retain their magnetic performance and reliability under challenging operating conditions.
-
05
High saturation flux density
Nanocrystalline cores offer high saturation flux density, meaning they can store and handle larger magnetic field strengths without saturating. This characteristic allows for the design of compact and lightweight magnetic components that can handle high power levels.
-
06
Reduced magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is the phenomenon where a material changes dimensions under the influence of a magnetic field, which can lead to mechanical stress and vibration. Nanocrystalline cores exhibit extremely low magnetostriction, resulting in reduced mechanical stress and vibration. This quality is particularly important in applications that require low noise and high mechanical stability.
-
07
Miniaturization and weight reduction
Nanocrystalline cores can be manufactured in smaller sizes while maintaining their excellent magnetic properties. This feature enables the design of smaller, lighter, and more compact magnetic components, making them suitable for miniaturized electronic devices and applications where space and weight are critical factors.
Applications
-

Solar inverters
-

New energy vehicles
-

Current transformer
-

High efficient transformer
-

APF
-

Energy Storage Power Station
-

Rail Transit