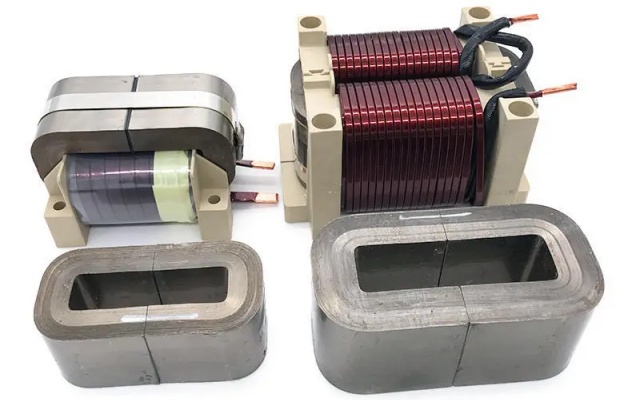
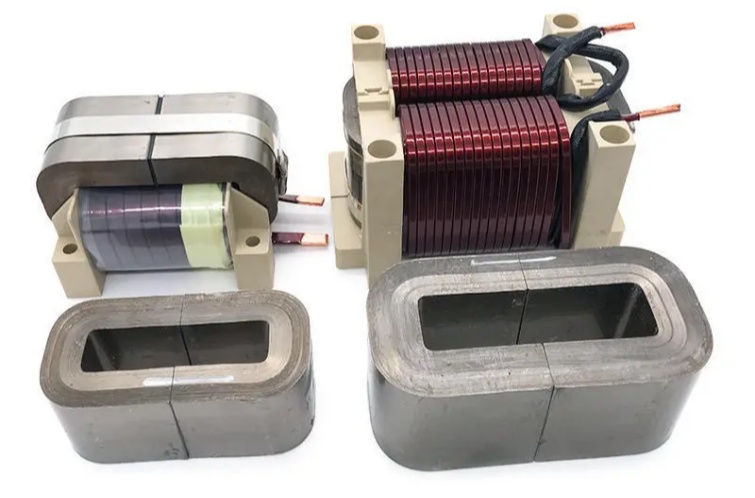
- Feature
- Performance
- Curve Comparison Chart
- Advantage
- Applications
- Video
Feature
Feature Description
Reduced distribution and core losses;
Wide range of frequency properties;
Excellent resistance to corrosion;
Low temperature rise.

Performance

High magnetic permeability
Amorphous cores typically have high permeability, which is a measure of how easily a material can be magnetized. High permeability allows for efficient magnetic coupling and improved performance in applications such as transformers, inductors, and magnetic sensors.
Low core loss
Amorphous cores have significantly lower core losses compared to traditional crystalline magnetic cores.This characteristic makes amorphous cores suitable for high-efficiency power conversion applications, such as transformers, inductors, and magnetic components in power electronics.
Excellent Temperature Stability
Amorphous cores exhibit excellent temperature stability, maintaining their magnetic properties over a wide temperature range. They can operate reliably at elevated temperatures without significant performance degradation. This characteristic makes amorphous cores suitable for high-temperature applications, where stable magnetic behavior is required.
Wide Frequency Response
Amorphous cores have a wide frequency response, covering a broad range of frequencies without significant degradation in their magnetic properties. This characteristic makes them suitable for applications that require operation in a wide frequency range, such as power supplies, inverters, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters.
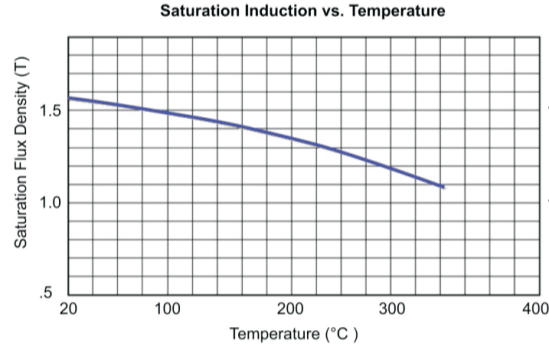
High saturation magnetic induction intensity
Amorphous cores possess high saturation flux density, which refers to the maximum magnetic flux density a material can withstand before losing its magnetic properties. This means that amorphous cores can store more magnetic energy and handle higher magnetic fields. The high saturation flux density allows for the design of compact and lightweight magnetic components that can handle high power levels.
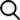
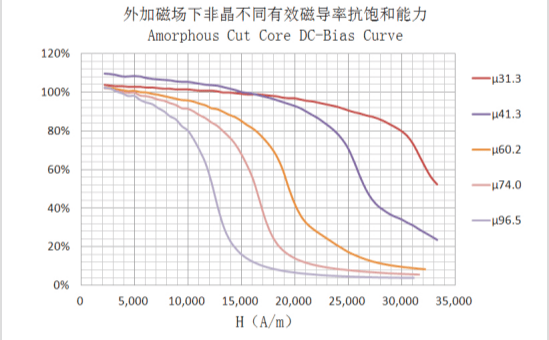
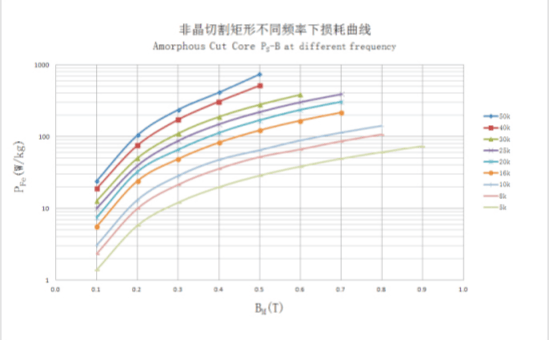
Curve Comparison Chart
Advantage
-
01
Reduced size and weight
Due to their unique atomic structure, amorphous cores can be manufactured into thin ribbons or smaller sizes, resulting in compact and lightweight magnetic components. This feature is particularly advantageous for miniaturized electronic devices and applications with space constraints.
-
02
Low core loss
Amorphous cores have extremely low core losses, which refer to the energy dissipation that occurs within the core during the magnetization and demagnetization processes. The disordered atomic structure of amorphous materials reduces hysteresis and eddy current losses, resulting in significantly lower core losses compared to crystalline cores. This leads to higher energy efficiency and reduced heating in applications such as transformers and inductors.
-
03
Improved manufacturing flexibility
Amorphous cores can be easily produced using techniques such as rapid solidification or melt spinning, allowing for efficient and cost-effective mass production. The flexibility in manufacturing processes enables customized designs and shapes to meet specific application requirements.
-
04
Excellent temperature stability
Amorphous cores exhibit excellent temperature stability, maintaining their magnetic properties over a wide temperature range. They can operate reliably at higher temperatures without significant degradation, making them suitable for applications that require elevated temperature operation.
-
05
High saturation flux density
Amorphous cores exhibit high saturation flux density, which is the maximum magnetic flux density a material can withstand before losing its magnetic properties. This property allows amorphous cores to store a larger amount of magnetic energy and handle higher magnetic fields, making them suitable for applications that require high-power and high-performance magnetic components.
-
06
Wide frequency response
Amorphous cores have a wide frequency response, meaning they can maintain stable magnetic properties over a broad range of frequencies. This characteristic makes them well-suited for applications in power electronics, where operation at various frequencies is common.
Applications
-

Reactor cores for PV inverter
-

Filter reactor of DC/DC in EV
-

AC and DC transformers
-

Mid-high frequency transformer
-

APF
-

Energy Storage Power Station
-

Rail Transit